Summary
Use of a remote monitoring (RM) program in patients with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) or cardiac resynchronization therapy-defibrillator (CRT-D) was associated with increased survival, regardless of device type and socioeconomic status. This article presentz data from a study of adherence to remote monitoring of patients with a pacemaker or defibrillator.
- Cardiology Clinical Trials
- Arrhythmias
- Interventional Techniques & Devices
- Cardiology Clinical Trials
- Arrhythmias
- Cardiology & Cardiovascular Medicine
- Interventional Techniques & Devices
Use of a remote monitoring (RM) program in patients with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) or cardiac resynchronization therapy-defibrillator (CRT-D) was associated with increased survival, regardless of device type and socioeconomic status. Suneet Mittal, MD, Valley Health System of New York and New Jersey, New York, New York, USA, presented data from a study of adherence to remote monitoring of patients with a pacemaker or defibrillator.
A previous study demonstrated that enrollment in a remote monitoring program was associated with improved survival in patients with an ICD or cardiac CRT-D [Saxon LA et al. Circulation 2010]. The purpose of this current study was to examine the association between adherence to remote monitoring and survival and to explore potential mechanisms between remote monitoring and improved outcomes.
In this prospective observational cohort study, patients (n=262,562) with a wireless pacemaker, CRT-pacemaker, ICD, or CRT-D device capable of remote monitoring with the Merlin.net Patient Care Network were followed from device implantation (between 2009 and 2011) to follow-up (up to November 2012). Device-tracking data included age, sex, implant date, device type, follow-up duration, and postal zip code. US Census data were used to link zip code to race, education level, employment status, health care insurance, median income, use of food stamps, and urban/rural classification.
The utilization of remote monitoring by patients was assessed weekly with http://Merlin.net. Adherence was defined as the number of total follow-up weeks that included a status transmission. Remote monitoring adherence was categorized as high (≥75%), low (between 0% and 75%), and none. The primary end point of interest was all-cause mortality.
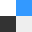
A larger proportion of patients with high utilization of remote monitoring survived when compared to patients with low utilization of remote monitoring (HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.47 to 1.59; p<0.001) or no utilization of remote monitoring (HR, 2.40; 95% CI, 2.32 to 2.49; p<0.001; Figure 1). In addition, patients with low adherence to remote monitoring were more likely to survive than patients who did not utilize remote monitoring (HR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.51 to 1.61; p<0.001). Remote monitoring adherence was associated with increased survival regardless of device type.
Proportion of Surviving Patients According to RM Adherence
RM=remote monitoring.
Reproduced with permission from S Mittal, MD.
In the United States, adherence rates were highest in the Midwest, South (excluding Florida), and the Pacific Northwest. In contrast, the lowest adherence rates appeared to be in the Northeast, the Chicago area, southern Florida, and California. Socioeconomic factors, such as unemployment, lack of health care insurance, use of food stamps, earnings below the poverty line, education level, and having a telephone, were not associated with adherence to remote monitoring.
In conclusion, Dr. Mittal stated that the data from this study showed that adherence to remote monitoring is associated with improved survival, irrespective of the type of implanted device. He highlighted that patients with high adherence to remote monitoring were associated with improved survival rates when compared with patients with either low or no adherence to remote monitoring. Dr. Mittal indicated that the results of this study suggest that adherence to remote monitoring is important.
- © 2014 MD Conference Express®