Summary
A pharmacodynamics study in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) reveals that sitagliptin QD provides greater inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) through the dosing interval (ie, measured at trough, 24 hours following the last morning dose) than either saxagliptin 5 mg QD or vildagliptin 50 mg QD and similar DPP-4 inhibition to vildagliptin 50 mg BID. The findings come from a randomized, placebo-controlled, open-label, crossover study.
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetes & Endocrinology Clinical Trials
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetes & Endocrinology Clinical Trials
- Endocrinology
- Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome
A pharmacodynamics study in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) reveals that sitagliptin QD provides greater inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) through the dosing interval (ie, measured at trough, 24 hours following the last morning dose) than either saxagliptin 5 mg QD or vildagliptin 50 mg QD and similar DPP-4 inhibition to vildagliptin 50 mg BID. The findings come from a randomized, placebo-controlled, open-label, crossover study presented by Harvey L. Katzeff, MD, Merck/MSD, Whitehouse Station, New Jersey, USA.
Because the soluble form of DPP-4 is shed into the circulation, measurement of DPP-4 activity in blood is possible. Inhibitors of DPP-4 are heterogeneous in structure and have different pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and DPP-4-binding characteristics. No direct comparison of DPP-4 inhibition among these agents using a single inhibition assay in the same cohort had been conducted prior to this study. An assay that minimized ex vivo plasma dilution was used to assess trough DPP-4 inhibition after the final dose following 5 days of administration of saxagliptin 5 mg QD, sitagliptin 100 mg QD, and vildagliptin 50 mg QD and BID regimens in a cohort of patients with T2DM (n=22). Trough DPP-4 inhibition for each of the four regimens and placebo control could be directly compared at 24 hours following the final morning dose. Eligible patients were required to have HbA1C levels of 6.5% to 10.0% (inclusive) either while treatment-naïve or after being washed off of prior antihyperglycemic medication.
In separate treatment periods, each participant received 5 days of either saxagliptin 5 mg QD, sitagliptin 100 mg QD, vildagliptin 50 mg QD, vildagliptin 50 mg BID, or placebo. Each participant was assigned to a randomized treatment sequence according to a computer-generated allocation schedule. Treatment periods were separated by at least 10 days. The randomized cohort included 12 women and 10 men with a mean HbA1C of 7.4% and mean age of 55 years.
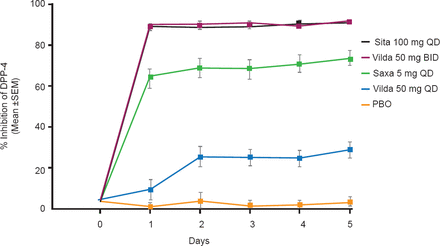
The percent DPP-4 inhibition was calculated for each treatment relative to the predose DPP-4 activity in each period. Sitagliptin QD and vildagliptin BID achieved >90% trough DPP-4 inhibition, reaching steady state within 1 day. In contrast, trough DPP-4 inhibition was 73.5% after saxagliptin QD and 28.8% after vildagliptin QD. The trough DPP-4 inhibition following placebo treatment was within 3.9% of the baseline measure (Figure 1). “DPP-4 inhibition ≥80% is believed to be necessary to achieve maximal efficacy of DPP-4 inhibitors”, said Dr. Katzeff.
Trough % Inhibition of DPP-4 Activity Over 5 Days
DPP-4=dipeptidyl peptidase-4; PBO=placebo.
Reproduced with permission from HL Katzeff, MD.
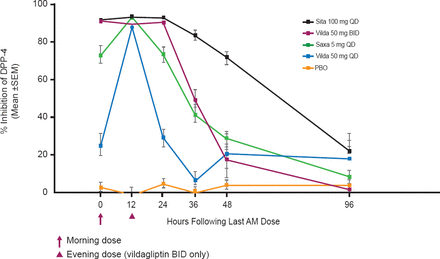
The time course of DPP-4 inhibition over 96 hours and following 5 days of administration favored sitagliptin 100 mg QD (Figure 2), which maintained DPP-4 inhibition of ∼92% over 24 hours that declined slowly over the following 24 to 96 hours. Vildagliptin 50 mg BID maintained >90% DPP-4 inhibition over 24 hours but inhibition declined rapidly over the following 12 to 24 hours. Saxagliptin 5 mg QD maintained ∼72% DPP-4 inhibition at 24 hours but inhibition also declined rapidly over the following 12 to 24 hours. Vildagliptin 50 mg QD achieved rapid DPP-4 inhibition but inhibition declined rapidly starting at 12 hours.
Percent Inhibition of DPP-4 Activity at 0–96 Hours
DPP-4=dipeptidyl peptidase-4; PBO=placebo.
Reproduced with permission from HL Katzeff, MD.
Ten adverse events were reported in 7 of the 22 patients, with headache the most commonly reported adverse event (6 events reported in 3 patients). All adverse events were mild or moderate in intensity and were transient in nature. There were no adverse events that led to patient withdrawal from the study.
Dr. Katzeff concluded that the three DPP-4 inhibitors studied provided significantly different trough levels of DPP-4 inhibition. Trough inhibition was submaximal in patients treated with saxagliptin 5 mg QD and vildagliptin 50 mg QD, whereas >90% DPP-4 inhibition was sustained throughout 24 hours in patients treated with sitagliptin 100 mg QD and vildagliptin 50 mg BID.
- © 2013 MD Conference Express®