Summary
AX200 was a novel and promising drug candidate with a comprehensive preclinical and clinical package that fulfilled Stroke Therapy Academic Industry Roundtable (STAIR) and European Stroke Organization recommendations; yet, no difference was observed in clinical outcome or imaging compared with placebo in acute ischemic stroke patients, according to results from the AX200 for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke Phase 3 trial [AXIS-2; NCT00927836].
- Cerebrovascular Disease Clinical Trials
AX200 was a novel and promising drug candidate with a comprehensive preclinical and clinical package that fulfilled Stroke Therapy Academic Industry Roundtable (STAIR) and European Stroke Organization recommendations; yet, no difference was observed in clinical outcome or imaging compared with placebo in acute ischemic stroke patients, according to results from the AX200 for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke Phase 3 trial [AXIS-2; NCT00927836]. E. Bernd Ringelstein, MD, Westfälische Wilhelms Universität Münster, Münster, Germany, reported outcomes from the study.
AXIS 2 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-arm, multinational, multicenter trial that included 328 patients with acute ischemic stroke in the middle cerebral artery territory. The objective was to demonstrate the efficacy of AX200 (rhG-CSF; filgrastim) versus placebo. The most relevant inclusion criteria were that patients had to be <9 hours from symptom onset, have a National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) of 6 to 22, have a diffusion-weighted imaging lesion >15 cm3, and be aged ≤85 years. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA) was allowed if patients were still eligible after lysis (ie, had an NIHSS of at least 6).
Patients were randomized to receive 135 μg/kg of AX200 over 72 hours intravenously or placebo, with one-third given over 30 minutes as a priming dose. The primary endpoint was modified Rankin scale (mRS) score at Day 90. The secondary endpoint was NIHSS at Day 90. Additional analyses were performed on infarct growth, adverse events, mortality, cytokines, and hematology.
The study was conducted at 51 sites in 7 countries. Intention-to-treat (ITT; n=323) and per-protocol analyses (n=272) were performed. Patients had a mean age of 63±10 years, and there were no significant differences in demographics. Hematology tests showed an expected increase in white blood cells and monocytes and a small decrease in platelets. No significant differences were observed in serious adverse events.
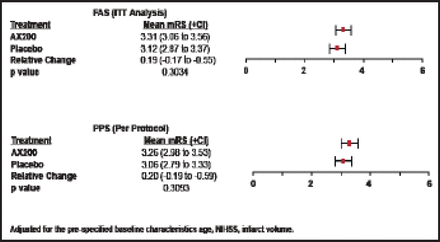
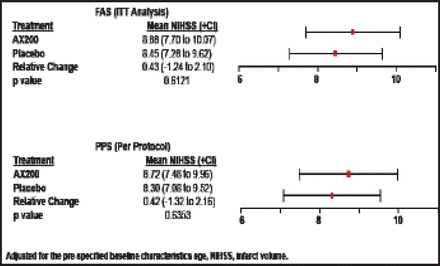
There were no significant differences between AX200 and placebo patients in the primary efficacy endpoint (mRS at Day 90) in either the ITT or per-protocol groups, and there was broad overlap in confidence intervals (Figure 1). The same outcome was seen in the secondary endpoint (NIHSS at Day 90; Figure 2). No significant differences between the AX200 and control groups were observed in the subgroup analysis for rtPA pretreatment, either.
mRS Day 90 AXIS200 Efficacy Endpoint.
Reproduced with permission from EB Ringelstein, MD.
NIHSS Day 90 AXIS200 Efficacy Endpoint.
Reproduced with permission from EB Ringelstein, MD.
The p value for mortality at 90 days was 0.4042 (Fisher's exact test); for the mRS Day 90 shift analysis, it was 0.2938, adjusted for the prespecified baseline characteristics, age, NIHSS, and infarct volume. There were no significant differences between the treatment and control groups in infarct volume.
As a stroke drug candidate, AX200 had a high validation level in animal studies (>30 publications in various stroke models), fulfilling STAIR criteria. AXIS Phase 2a data indicated that recombinant granulocyte colony-stimulating factor is well tolerated and safe in acute stroke.
Safety and tolerability were confirmed in AXIS 2, and showed the predicted pharmacokinetic and pharmacokinetic profile of AX200 in the blood. However, there were no differences between AX200 and placebo treatment in clinical outcome or imaging. No reasons for the failure are evident at present, but data analyses are ongoing.
- © 2012 MD Conference Express®