Summary
The International Breast Cancer and Nutrition (IBCN) Project was launched in 2010 and is the first global effort to elucidate the relation between diet, genetics, and the development of breast cancer. This article reviews new research approaches for the IBCN and some preliminary data from Phase 1 of the study on the primary prevention of breast cancer and other noncommunicable diseases.
- nutrition physiology
- breast cancer
- nutrigenomics
The International Breast Cancer and Nutrition (IBCN) Project was launched in 2010 and is the first global effort to elucidate the relation between diet, genetics, and the development of breast cancer. It will also serve as a model for the study of primary prevention of breast cancer and other noncommunicable diseases. Ailsa Welch, PhD, University of East Anglia, Norwich, United Kingdom, reviewed new research approaches for the IBCN and some preliminary data from Phase 1 of the study.
The IBCN is managed by researchers at Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA, and participation is voluntary. Currently, 11 countries are participating in the IBCN (including China, Lebanon, France, Ghana, Qatar, the United Kingdom, the United States, and Uruguay), which provides a diverse range of dietary exposure and patterns.
Multidisciplinary teams at the participating centers are collecting diet information, breast tissue, and blood samples. Novel approaches are being used to more accurately capture dietary intake, diet composites, and measurement of biomarkers and nutrient status that are indicators of nutritional exposure. The goal is to better understand the relationship between diet and genetics through the study of tissue samples from patients with breast cancer.
The experience from the European Prospective Investigation Into Cancer and Nutrition [EPIC], which began in 1993 and included 10 countries and 450,000 participants, gave investigators important experience and has helped to overcome some of the methodological challenges being experienced in IBCN. These solutions include the development of standardized nutrient databases, a biomarker validation program, and dietary calibration that included the development of a standardized computer program for 24-hour dietary recall interviews. Prof. Welch noted that these solutions within EPIC were highly labor and resource intensive.
A Phase 1 proof-of-principle study in IBCN has demonstrated that the project is feasible, said Prof. Welch. The objective of Phase 1 was to test the process to collect international samples. It also included designing one or two dietary patterns that represented common eating patterns in the research region that are representative of national data and reflect the appropriate energy intake for a woman between 18 and 45 years old.
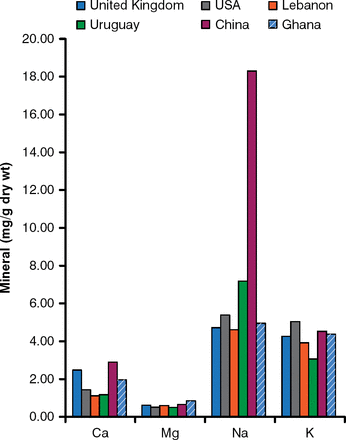
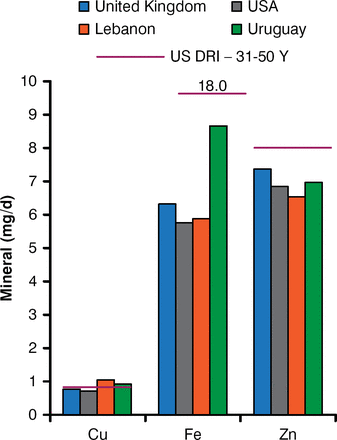
The intake of calcium, magnesium, sodium, and potassium in six countries based on dietary patterns submitted in Phase 1 is shown in Figure 1, and the intake of copper, iron, and zinc is shown in Figure 2.
Mineral Intake in the Phase 1 Study in 6 Countries
Ca=calcium; K=potassium; Mg=magnesium; Na=sodium.
Reproduced with permission from A Welch, MD.
Intake of Copper, Iron, and Zinc in the Phase 1 Study
Cu=copper; DRI=daily recommended intake; Fe=Iron, Zn=zinc.
Reproduced with permission from A Welch, MD.
The Phase 2 proof-of-principle study is currently underway. Lessons learned from Phase 1 have presented opportunities to refine the processes for Phase 2 and subsequent research by the IBCN. Phase 1 of the study highlighted the need for adequate protocol training, because simply providing a protocol to investigators was insufficient because of differences in cultures and disciplines among countries. Improvements must be made in the documents and instructions to reduce variation in the types of information (eg, weights and menus) received with the diet shipments. Finally, the requirements for ethics approval varied greatly among countries, with some requiring a proposal for the entire project and a literature review, which resulted in a process that was slow and complicated.
Extensive progress has been made in establishing the IBCN project, stated Prof. Welch, providing a foundation to move on to the next research stages and expand the number of participating countries and researchers.
- © 2014 MD Conference Express®