Summary
This article presents the results of the Efficacy at 24 Weeks and Long-Term Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy up to 2 Years of Secukinumab (AIN457) in Patients With Active Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) study [FUTURE 1; NCT01392326]. FUTURE 1 is a multicenter, placebo-controlled phase 3 study in which 606 patients with PsA received an intravenous loading dose of secukinumab at 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks for the first 4 weeks, followed by subcutaneous doses of 75 mg (n=202) or 150 mg (n=202) monthly, compared with placebo (n=202).
- Inflammatory Disorders Rheumatology Clinical Trials
- Arthritis
- Inflammatory Disorders
- Rheumatology
- Rheumatology Clinical Trials
- Arthritis
For patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), treatment with secukinumab confers rapid clinical improvements in signs, symptoms, physical function, quality of life, and inhibition of radiographic disease progression.
Philip Mease, MD, Swedish Medical Center and University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, USA, presented the results of the Efficacy at 24 Weeks and Long-Term Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy up to 2 Years of Secukinumab (AIN457) in Patients With Active Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) study [FUTURE 1; NCT01392326].
FUTURE 1 is a multicenter, placebo-controlled phase 3 study in which 606 patients with PsA received an intravenous loading dose of secukinumab at 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks for the first 4 weeks, followed by subcutaneous doses of 75 mg (n = 202) or 150 mg (n = 202) monthly, compared with placebo (n = 202).
The primary end point of the study was the American College of Rheumatology 20% improvement response criteria (ACR20), indicating ≥ 20% improvement in signs and symptoms of PsA, at week 24.
Secondary end points included 75% and 90% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI 75 and PASI 90), change from baseline in 28-joint Disease Activity Score (DAS28) using C-reactive protein (CRP), physical function assessed by SF-36 Health Survey physical component summary scores and by the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), ACR 50%/70% improvement response criteria (ACR50/70) response, proportion of patients with dactylitis and enthesitis, and overall safety and tolerability.
Of 606 patients, more than half were women, and the average age was 49 years. The mean weight was about 84 kg, and about 80% of patients were white.
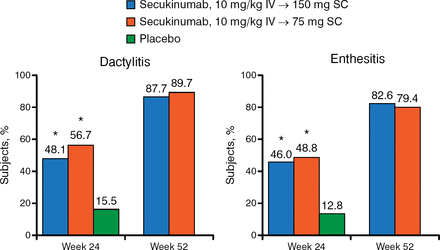
The study found that significantly more patients achieved ACR20 response at week 24 than placebo (50.5% and 50.0% for secukinumab 75- and 150-mg treatment arms vs 17.3% for placebo; P < .0001). In addition, patients treated with secukinumab had improved clinical benefit as measured by the secondary end points.
Dr Mease focused some of his presentation on an exploratory analysis of FUTURE 1 that looked at the extended outcomes beyond week 24 to week 52. The study found that most of the patients treated with secukinumab at 75 mg and 150 mg who achieved ACR20 responses at week 24 also maintained the response at week 52 with continuation of treatment (66.9% and 69.5%, respectively; Figure 1).
Sustained Response to Secukinumab at Week 52
Missing values were imputed as nonresponse (nonresponder imputation) up to week 24. Observed data from week 28 to 52.
IV, intravenous; SC, subcutaneous.
*P < .0001 vs placebo (P values at week 24 adjusted for multiplicity of testing).
Reproduced with permission from P Mease, MD.
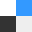
The clinical benefits of secukinumab also extended to week 52 when looking at secondary end points, including PASI 75 and PASI 90, DAS28-CRP, resolution of dactylitis and enthesitis, HAQ-DI scores, SF-36 scores, and ACR50/70. For example, ACR50 responses at week 24 were 34.7% and 30.7% for patients treated with 150 mg and 75 mg of secukinumab and were sustained at 50.0% and 38.4%, respectively, at week 52. The ACR70 responses at week 24 were 18.8% and 16.8%, respectively, and 28.2% and 25.6%, respectively, at week 52 (Figure 2).
Resolution of Dactylitis and Enthesitis at Weeks 24 and 52
IV, intravenous; SC, subcutaneous.
*P < .0001 vs placebo.
Reproduced with permission from P Mease, MD.
Serious infections occurred at the rate of 2.9, 2.6, and 1.4 events per 100 patient-years in the 150-mg, 75-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. Dr Mease highlighted a few cases of mild to moderate candida infections and neutropenia, adverse events known to be specifically related to IL-17 inhibition. Dr Mease stated that based on the overall safety data, secukinumab is overall well tolerated with no unexpected safety findings and low immunogenicity.
- © 2014 MD Conference Express®