Summary
Moderate to severe plaque psoriasis has both physical and psychological effects, leading to major impairment of health-related quality of life. Tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, was found to be effective in A Phase 3, Multi Site, Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Study of the Efficacy and Safety Comparing CP- 690,550 and Etanercept in Subjects With Moderate to Severe Chronic Plaque Psoriasis [NCT01241591]. The objective of this analysis of the tofacitinib phase 3 trial was to assess the effects of tofacitinib (5 and 10 mg, BID) versus etanercept or placebo on patient-reported outcomes.
- Dermatology Clinical Trials
- Skin Diseases
- Dermatology Clinical Trials
- Skin Diseases
- Dermatology
Moderate to severe plaque psoriasis has both physical [Strand V et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; Reich A et al. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010] and psychological effects [Kurd SK et al. Arch Dermatol. 2010; Kimball AB et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2005], leading to major impairment of health-related quality of life (QOL). Tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, was found to be effective in A Phase 3, Multi Site, Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Study of the Efficacy and Safety Comparing CP-690,550 and Etanercept in Subjects With Moderate to Severe Chronic Plaque Psoriasis [NCT01241591].
The objective of this analysis of the tofacitinib phase 3 trial, presented by Fernando Valenzuela, MD, University of Chile Clinical Hospital, Santiago, Chile, was to assess the effects of tofacitinib (5 and 10 mg, BID) versus etanercept or placebo on patient-reported outcomes. After a 4-week screening period, patients with psoriasis for ≥ 12 months were randomized 3:3:3:1 to tofacitinib, 5 mg (n = 330) or 10 mg (n = 332) BID, plus subcutaneous (SC) placebo twice weekly; etanercept, 50 mg, SC, twice weekly plus placebo BID (n = 336); or placebo BID plus SC placebo twice weekly (n = 108). The patients were stratified by the number of failed prior systemic therapies.
The main inclusion criteria were as follows: Psoriasis Area Severity Index ≥ 12; Physician's Global Assessment of moderate or severe psoriasis; psoriasis on ≥ 10% of the body surface area; and failed, intolerant, or contraindication to ≥ 1 systemic therapy (≥ 2 in some countries). Patients with nonplaque or drug-induced psoriasis or evidence of active infection were excluded. The patient-reported outcome end points assessed at week 12 were as follows: Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), Itch Severity Item (ISI), Patient Global Assessment (PtGA), and Patient Satisfaction With Study Medication (PSSM).
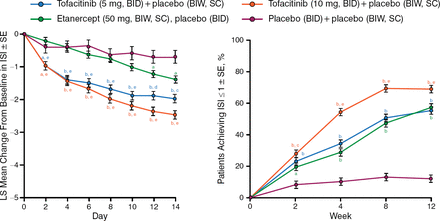
Baseline patient demographics and disease characteristics were well balanced across the treatment groups. The mean baseline scores on several end points (including the DLQI, ISI, and PtGA) indicated a substantial disease burden on QOL in this patient population. The patients in both tofacitinib dosage groups experienced a rapid, significant improvement in itch severity as early as day 2 (P < .05; Figure 1). From week 2, among patients with a baseline ISI > 1, all active treatment groups had a significantly greater percentage of patients with ISI ≤ 1 (little to no itching) vs placebo (P < .0001).
Itch Severity Item Score Showed Rapid Improvement With Tofacitinib
BIW, twice weekly; ISI, Itch Severity Item; LS, least squares; SC, subcutaneous; SE, Standard error.
a P <.05 vs placebo; b P <.0001 vs placebo; c P <.05 vs etanercept; d P <.001 vs etanercept; e P <.0001 vs etanercept.
Reproduced with permission from F Valenzuela, MD.
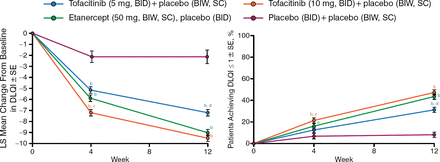
At weeks 4 and 12, the mean DLQI score demonstrated significant improvement from baseline with tofacitinib (5 and 10 mg) and etanercept (50 mg) vs placebo (P < .0001 for all vs placebo at weeks 4 and 12; Figure 2). Among patients with baseline DLQI > 1, significantly more patients receiving active treatment reported DLQI ≤ 1 (no effect of psoriasis on QOL) vs placebo (P < .0001).
Dermatology Life Quality Index Score Improved With Tofacitinib
BIW, twice weekly; DLQI, Dermatology Life Quality Index; LS, least squares; SC, subcutaneous; SE, standard error.
a P <.05 vs placebo; b P <.0001 vs placebo; c P <.05 vs etanercept; d P <.001 vs etanercept.
Reproduced with permission from F Valenzuela, MD.
From week 4, significantly more patients receiving active treatment reported a PtGA of “clear” or “almost clear” versus those receiving placebo (P < .0001). More than 50% of patients receiving tofacitinib (10 mg) or etanercept achieved a PtGA of “clear” or “almost clear.” More than 70% of patients receiving active treatment were satisfied with their treatment at week 12, as assessed by the PSSM.
The results of this study demonstrated that patients treated with tofacitinib (5 or 10 mg, BID) exhibited significant improvement across multiple measures of health-related QOL when compared with placebo. These results suggest that oral tofacitinib may be an effective new treatment option for patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis.
- © 2014 MD Conference Express®